

This article lists the oldest known surviving buildings constructed in the Americas, including on each of the regions and within each country."Building" is defined as any human-made structure used or interface for supporting or sheltering any use or continuous occupancy. In order to qualify for this list a structure must:
| width=180 | Building | Image | width=90 | Location | width=140 | Country or territory | data-sort-type=number | First built | Use | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sechin Bajo | Áncash |  | 3500 BCE | Administrative-ceremonial center | A large archaeological site with ruins dating from 3500 BCE to 1300 BCE.[1] | |||||
| Pyramids of Caral | Lima |  | 2600 BCE | Temples and houses | Built by the Caral civilization, these pyramids predate the Egyptian pyramids by around 100 years.[2] | |||||
| Los Naranjos | Yojoa |  | 2000 BCE | Temples | Oldest man built structures still surviving in Honduras constructed by ancestors of the Lencan people.[3] | |||||
| Kotosh | Huánuco |  | 1800 BCE | Temple | Archaeological site consisting of buildings with six periods of continuous occupation.[4] | |||||
| La Venta | Tabasco |  | 1700 BCE | Temples | Oldest structures in the state of Tabasco Mexico. | |||||
| El Chircal | La Paz |  | 1400 BCE | Ceremonial center | Pyramids of the pre-Classic period built by the Lencan people. | |||||
| Lima |  | 1400 BCE | Temples | One of the largest centers of pre-Columbian culture on Peru's central coast.[5] | ||||||
| Yucuita | Oaxaca |  | 1300 BCE | Ceremonial center and a square | Founded by the Mixtec civilization in the pre-Classic Period[6] | |||||
| San José Mogote | Oaxaca |  | 1300 BCE | Town | San José Mogote was the largest and most important Zapotec settlement in the Valley of Oaxaca during the Early and Middle Formative periods. | [7] | ||||
| Chavín de Huantar | Áncash |  | 1200 BCE | Religious center | Occupation at Chavín de Huántar by the Chavín people has been carbon dated to at least 3000 BCE.[8] | |||||
| Garðar Cathedral Ruins | Igaliku |  | 1126 CE | Cathedral | Oldest extant building of European origin in North America.[9] | |||||
| Hvalsey Church | Hvalsey |  | 1300 CE | Church | The best preserved Norse ruins in Greenland. |
| Building | Image | Location | Country or territory | data-sort-type="number" | First built | Use | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casa del Cordón | Santo Domingo |  | 1502–1503 | Isabelline Gothic house | Oldest European stone house in the Americas and probably the first European two-story house.[10] [11] [12] | ||
| Remaining sections of the Santo Domingo City Walls | Santo Domingo |  | 1502–1508 | Fortification | Oldest military construction of European origin in the Americas.[13] | ||
| Hospital San Nicolás de Bari | Santo Domingo |  | 1503 | Hospital | Oldest hospital in the Americas. In ruins.[14] | ||
| Monasterio de San Francisco | Santo Domingo |  | 1509–1560 | Monastery | Oldest monastery in the Americas. | ||
| Church and Convent of los Dominicos | Santo Domingo |  | 1510-1532 | Convent and University | Oldest Catholic building in continuous use in the Americas, and also, it was the headquarters of the first university in the Americas.[15] [16] | ||
| Basilica Cathedral of Santa María la Menor | Santo Domingo |  | 1514-1541 | Cathedral | First and oldest cathedral in the Americas, excluding Greenland.[17] [18] | ||
| Palace of Cortés | Cuernavaca |  | 1523–1528 | Palace | Oldest extant colonial-era civil structure in the continental Americas.[19] [20] | ||
| La Paz Centro | 1524 | Town | Oldest colonial buildings in Nicaragua | ||||
| Church of San José | San Juan |  | 1532–1735 | Church | Oldest extant building in Puerto Rico & the United States.[21] [22] | ||
| La Fortaleza | San Juan |  | 1533-1540 | Oldest official residence in the Americas.[23] | |||
| Catedral Metropolitana Basílica de San Juan Bautista | San Juan, Puerto Rico | 1540 | Cathedral | Oldest extant Cathedral in Puerto Rico & the United States.[24] Original founding & wood structure of church dates to 1521 | |||
| Iglesia de Balbanera | Cajabamba |  | 1534 | Church | Oldest extant building in Ecuador. | ||
| Iglesia de La Merced | Granada |  | 1534 | Church | Oldest extant building in Nicaragua.[25] | ||
| Church of Saints Cosme and Damião | Igarassu |  | 1535 | Church | Oldest extant building in Brazil.[26] | ||
| Cathedral Basilica of Lima | Lima |  | 1535-1649 | Cathedral | Oldest extant building in Peru.[27] | ||
| Colegio de Santa Cruz de Tlatelolco | Mexico City |  | 1536 | College | First and oldest European school of higher learning in the Americas. First major school of interpreters and translators in the Americas.[28] [29] | ||
| Monasterio de Santo Domingo | Guatemala City | 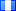 | 1538 | Monastery | Oldest extant building in Guatemala. In ruins.[30] | ||
| Real Audiencia de Gracias | Gracias | 1544 | Government building | Oldestadministratrive building extant in Honduras.[31] | |||
| Santa Barbara Fortress | Trujillo |  | 1550-1553 | Fortification | Oldest military construction of European origin on the American mainland.[32] | ||
| Iglesia de San Francisco | Bogotá |  | 1557–1566 | Church | Oldest extant building in Colombia.[33] | ||
| Castle de la Real Fuerza | Havana |  | 1558–1577 | Fortification | It is considered to be the oldest stone fort in the Americas. | ||
| Metropolitan Cathedral of Sucre | Sucre | 1559-1712 | Cathedral | Oldest extant building in Bolivia.[34] | |||
| La Merced Church | Comayagua |  | 1550-1561 | Church | Oldest church still standing in Honduras[35] | ||
| Immaculate Conception Cathedral | Comayagua | 1563-1715 | Cathedral | Oldest cathedral still standing in Honduras.[36] [37] | |||
| Iglesia de Nuestra Señora de la Asunción | Izalco |  | 1569 | Church | Oldest extant building in El Salvador. In ruins.[38] | ||
| Iglesia de Nuestra Señora de la Limpia Concepción | Ujarrás |  | 1580s | Church | Oldest extant building in Costa Rica. Partially restored.[39] [40] | ||
| Castillo San Felipe del Morro | San Juan, Puerto Rico | 1589 to 1650 | Fortification | Oldest extant masonry fortification construction in Puerto Rico[41] & the United States. |
| width=180 | Building | Image | width=90 | Location | width=140 | Country or territory | data-sort-type=number | First built | Use | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palace of the Governors | Santa Fe |  | 1610–1618 | Palace | Oldest extant building in the contiguous United States.[42] | |||||
| King's Castle | St. George's Parish |  | 1612 | Fortification | Ruined King's Castle ("Queen's Castle" during the reigns of Queens Anne and Victoria, and also called "Seaward Fort") on Castle Island (including its Captain's house, the oldest surviving dwelling house in Bermuda). Oldest extant building in Bermuda.[43] | |||||
| Iglesia de San Francisco | Santiago |  | 1618 | Church | Oldest extant building in Chile.[44] | |||||
| State House | St. George's Town |  | 1620 | House of Assembly | The State House was the first purpose-built home of the House of Assembly, which then constituted the only chamber of the Parliament of Bermuda. Other than fortifications, it was Bermuda's first stone building. It is the oldest surviving Bermudian building, again excepting some fortifications (St. Peter's Church was established in 1612, but rebuilt several times and its oldest parts are thought to date from the 1620s), and has been used since 1815 as a Masonic lodge. | |||||
| St. Peter's Church | St. George's Town |  | 1620s (established 1612) | Church | Oldest Protestant church in the "New World" (the Americas and certain Atlantic islands such as Bermuda). St. Peter's Church was the first of nine Parish churches established in Bermuda by the Church of England. It was originally built in 1612, but rebuilt several times and its oldest parts today are thought to date from the 1620s. The House of Assembly of Bermuda met in the church pending completion of the State House. | |||||
| Carr's Bay Gun Battery | Little Bay |  | 1624 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Montserrat. | |||||
| Fort Amsterdam | Philipsburg | 1631 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Sint Maarten and on the island of Saint Martin. | ||||||
| Fort Amsterdam | Willemstad | 1634 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Curaçao. Founded by the Dutch West India Company.[45] | ||||||
| Fort Oranje | Kralendijk | 1639 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Bonaire.[46] | ||||||
| Le Carbet |  | 1640 | Residence | Oldest building in Martinique. In ruins.[47] Located within the Martinique Zoo.[48] | ||||||
| Ursulines of Quebec | Quebec City, Quebec |  | 1641–1642 | Monastery | Oldest extant building in Canada. Oldest institution of learning for women in North America.[49] | |||||
| St. Thomas' Lowland Church | Saint Thomas Lowland Parish |  | 1643 | Church | Oldest extant building in Saint Kitts and Nevis.[50] | |||||
| Biblioteca Palafoxiana | Puebla City |  | 1646–1773 | Library | First and oldest public library in the Americas.[51] [52] [53] | |||||
| Drax Hall | Saint George |  | 1650s | Residence | Possibly the oldest extant building in Barbados.[54] | |||||
| Fort Zeelandia | Paramaribo |  | 1651 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Suriname.[55] | |||||
| St Nicholas Abbey | Saint Peter |  | 1658 | Residence | Oldest extant building in Barbados with a verifiable date of construction.[56] | |||||
| Fort Morgan Cay | Roatán | 1667 | Fortification | Oldest building of european origin in the Bay Islands in ruins. | ||||||
| Fort Christian | Charlotte Amelie | 1672–1680 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in the United States Virgin Islands. | ||||||
| Castillo de San Marcos | St. Augustine, Florida |  | 1672–1695 | Fortification | Oldest extant masonry fortification in the contiguous United States. | |||||
| White Horse Tavern | Newport, Rhode Island |  | 1673 | Tavern | Oldest extant tavern in the Americas.[57] | |||||
| Iglesia de la Merced | Panama City |  | 1680 | Church | Oldest extant building in Panama.[58] | |||||
| Halse Hall | Clarendon Parish |  | 1680 | Residence | Oldest extant building in Jamaica.[59] [60] | |||||
| St. Ignatius Church | Buenos Aires |  | 1686-1722 | Church | Oldest extant building in Argentina. |
| width=180 | Building | Image | width=90 | Location | width=140 | Country or territory | data-sort-type=number | First built | Use | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grenada National Museum | St. George's |  | 1704 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Grenada. Served as a French barracks, British women's prison, hotel, warehouse, and is currently a museum.[61] [62] | |||||
| Saint-Claude | 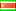 | 1726 | Residence | Oldest extant building in Guadeloupe.[63] | ||||||
| Mikvé Israel-Emanuel Synagogue | Willemstad | 1730 | Synagogue | Oldest extant synagogue in the Americas.[64] | ||||||
| Fort Saint-Joseph | Fort-Liberté |  | 1735–1743 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Haiti.[65] | |||||
| Fort Montagu | Nassau |  | 1741–1742 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in the Bahamas.[66] | |||||
| Fort Zeelandia | Essequibo Islands-West Demerara |  | 1743 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Guyana. In ruins.[67] Fort Kyk-Over-Al is older (built in 1616) but no longer fits the definition of a building. | |||||
| French Guiana Prefecture Building | Cayenne |  | 1749–1752 | Monastery | Oldest extant building in French Guiana. Currently serves as the seat of the Prefect of French Guiana.[68] | |||||
| Court House | St. John's |  | 1750 | Courthouse | Oldest extant building in Antigua and Barbuda.[69] | |||||
| Viola House | Asunción |  | 1750–1758 | Residence | Oldest extant building in Paraguay. | |||||
| Sambro Island Light | Sambro Island, Nova Scotia |  | 1758 | Lighthouse | Oldest extant lighthouse in the Americas.[70] | |||||
| Fort James | Plymouth |  | 1762 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Trinidad and Tobago.[71] | |||||
| Sandy Hook Light | Sandy Hook, New Jersey |  | 1764 | Lighthouse | Oldest extant lighthouse in the United States.[72] | |||||
| Fort Young | Roseau |  | 1770 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Dominica. Partially converted to a hotel in 1964.[73] [74] | |||||
| Fort Rodney | Pigeon Island |  | 1779–1782 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Saint Lucia.[75] | |||||
| Pedro St. James Castle | Grand Cayman |  | 1780 | Residence | Oldest extant building in the Cayman Islands. Restored in 1996.[76] | |||||
| Governors' House | Gustavia | 1780 | Residence | Oldest extant building in Saint Barthélemy. Originally a private residence, it became the Governors' House of Saint Barthélemy in 1785. | ||||||
| Wallblake House | The Valley |  | 1787 | Residence | Oldest extant building in Anguilla.[77] | |||||
| Fort Louis | Marigot | 1789 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Saint Martin. | ||||||
| Wade's Green Plantation | North Caicos |  | 1789 | Residence | Oldest extant building on the Turks and Caicos Islands. In ruins.[78] [79] | |||||
| Montevideo Metropolitan Cathedral | Montevideo |  | 1790–1804 | Cathedral | Oldest extant building in Uruguay. | |||||
| Fort Zoutman | Oranjestad |  | 1796–1798 | Fortification | Oldest extant building in Aruba. Founded by the Dutch West India Company. | |||||
| House of Assembly | Kingstown |  | 1798 | Parliament | Oldest extant building in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.[80] |
| width=180 | Building | Image | width=90 | Location | width=140 | Country or territory | data-sort-type=number | First built | Use | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russian-American Magazin | Kodiak |  United States United States | 1805–1808 | General store | Oldest extant building of Russian origin in the Americas.[81] | |||||
| St. John's Cathedral | Belize City |  | 1812–1820 | Cathedral | Oldest extant building in Belize. | |||||
| Central Stores | Stanley | 1844 | General store | Oldest extant building in the Falkland Islands.[82] | ||||||
| Our Lady of Ardilliers Church | Miquelon-Langlade | 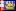 | 1862–1865 | Church | Oldest extant building in Saint Pierre and Miquelon.[83] [84] |